Point-of-Care Diagnosis
Due to its highly portable and cost-effective nature, microfluidic systems provide promising solutions for point-of-care and rapid analytics. We have developed several analytical platforms to achieve easy clinical sample handling as well as conducting single-cell-resolution cell phenotyping.
Topics
Blood Sample Processing Technologies
Rapid and accurate blood sample processing microfluidic methods
Selected Project/Publications
- A Circular Gradient-Width Crossflow Microfluidic Platform for High-Efficiency Blood Plasma Separation
H. Zhang, K. Anoop, C. Huang, R. Sadr, R. Gupte, J. Dai, and A. Han,
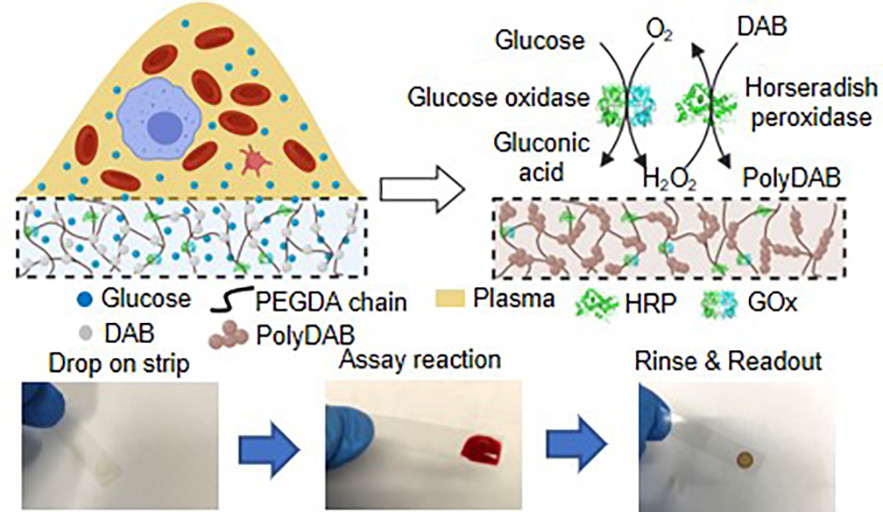
Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, Vol. 354 (1), 131180 (2022) - A Gel-based Separation-free Point of Care Device for Whole Blood Glucose Detection (cover article)
J. Dai*, H. Zhang*, C. Huang, Z. Chen, and A. Han (*these authors contributed equally),
Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 92, pp. 16122-16129 (2020)
Click here for cover image - Fabrication Methods for a Gel-Based Separation-Free Device for Whole Blood Glucose Detection
H. Zhang*, Y. Yang*, J. Dai, and A. Han (*these authors contributed equally),
MethodsX, Vol. 8, 101236 (2021) - A CFD-based design of a microfluidic platform for separating blood cells
A Kanjirakat, Z Han, R Sadr, and A Han, [at Qatar Collaboration],
APS Division of Fluid Dynamics Meeting Abstracts, L29. 001 (2019)
Cancer Cell Analyses
Innovative cancer cell analyses microfluidic systems.

Selected Project/Publications
- A Disposable Microfluidic Flow Sensor with a Reusable Sensing Substrate
J. Kim, H. Cho, S. -I. Han, A. Han, and K. -H. Han,
Sensors and Actuators: B. Chemical, Vol. 288, pp. 147-154 (2019) - A Continuous-Flow Acoustofluidic Cytometer for Single-Cell Mechanotyping
H. Wang, Z. Liu, D. M. Shin, Z. G. Chen, Y. Cho, Y. -J. Kim, and A. Han,
Lab on a Chip, Vol. 19, pp. 387-393 (2019) - Single-Cell Compressibility Quantification or Assessing Metastatic Potential of Cancer Cells
H. Wang, Z. Liu, D. M. Shin, Z. G. Chen, Y. Cho, Y. -J. Kim, and A. Han,
Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 22:68 (2018) - A Microchip for High-Throughput Axon Growth Drug Screening
58H. S. Kim, S. Jeong, C. Koo, A. Han, and J. Park,
Micromachines, Vol. 7 (7), 114 (2016) - Microfluidic Geometric Metering-based Multi-Reagent Mixture Generator for Robust Live Cell Screening Array
H. Wang, J. Kim. A. Jayaraman, and A. Han,
Biomedical Microdevices, Vol. 16, pp. 887-896 (2014)